Definition
The cereal and food may be contaminated by fungi. The best known are : Aspergillus, Penicillium and Fusarium. These are toxigenic fungal species. This term refers to a fungal species which some strains can produce, under certain conditions, one or more metabolites called mycotoxins. More than 300 of identified, but only 30 have toxic properties actually concern for human or animal. Mycotoxins can be toxic to humans and animals with varying degrees according to mycotoxins and the species.
Food contamination
In 1985, l’Organization of the United Nations for food and agriculture (FAO) felt that 25 % harvests of cereals in the world were affected by mycotoxins, which has the effect of reducing the food, both plant and animal, available at the global level. In addition, mycotoxins are responsible for sometimes fatal acute poisoning, especially among livestock, and chronic poisoning. The presence of certain contaminants genotoxic and carcinogenic in cereals and oilseeds affect doubling the food chain of human : via their direct consumption and the animals, but also by inhalation or skin contact. These risks are considered to be a major public health problem.
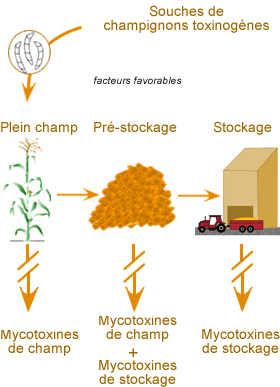
Common toxicity (MYCO-toxicity)
A species of microscopic fungus can generate multiple types of mycotoxins, and a same mycotoxin can be produced by several species of fungi. It has an acute effect (has the effect of accumulation of mycotoxins in a body such as the liver) or chronic on human. Hepatotoxic effects, neurotoxic, mutagenic, teratogenic, carcinogenic and immunosuppressive drugs have been proven experimentally in animals. These risks are still poorly known, but they are increasingly taken into account, by Community legislation which sets maximum limits of levels of mycotoxins in foods and breathe air. This concept of risk different mycotoxins of natural antibiotics, that must also be considered as belonging to the same family. One of the modes of action of mycotoxins would be the increase in the production of tartaric acid which, upon entering the Krebs cycle in competition with Malic acid decreases ATP production. This may be cause various symptoms such as asthenia or daytime Hypersomnia.

